I this blog post I’ll describe how to install and configure Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2012 from the scratch.
Why I chose to use Hyper-V Server 2012 in my production environment?
1. It’s free!
2. Less maintenance!
3. We don’t need to restart the host so often for the updates!
4. Performance and security reasons!
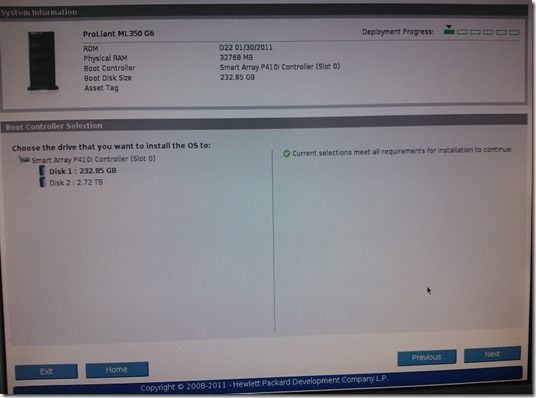
In this scenario I have HP ML 350G6 with 2 CPUs 32GB of RAM and 3TB disk.
HP have a great tool called HP SmartStart CD with integrated drivers and other tools required for server management, but in this case doesn’t work because WS 2012 and Hyper-V 2012 is not covered. I used this tool to create RAID array.
How do I integrate the drivers, (network, storage, etc…)? I used Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit software.
After a very short time, my Hyper-V Server 2012 is up and running.
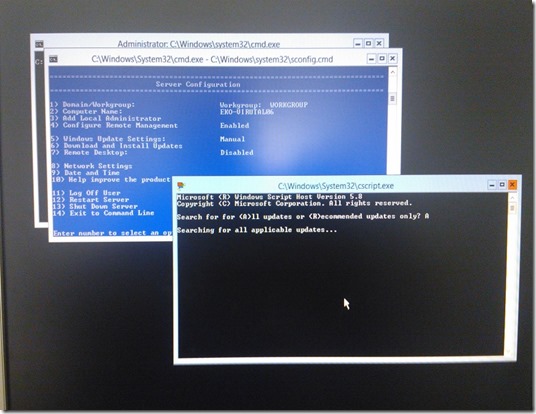
When Hyper-V Server 2012 console appears you can to configure Domain, Computer Name, Remote Management, Network Settings and so on….
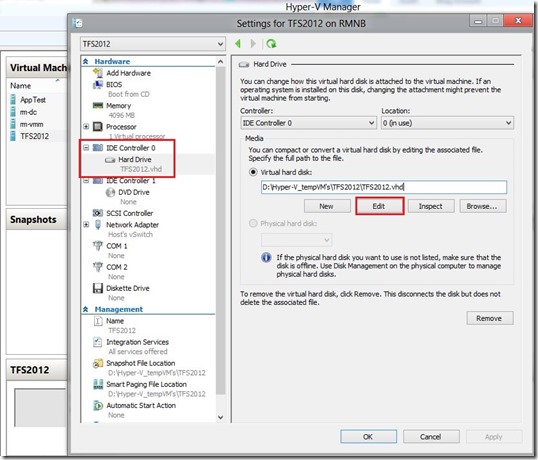
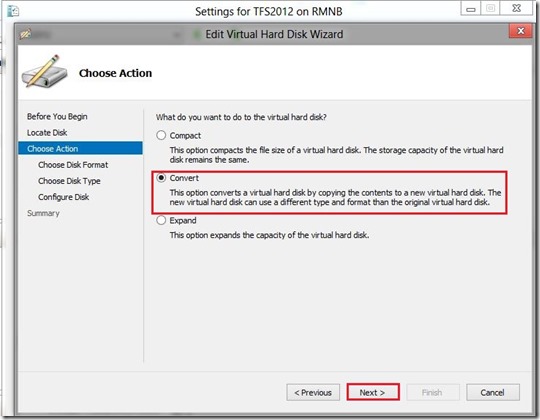
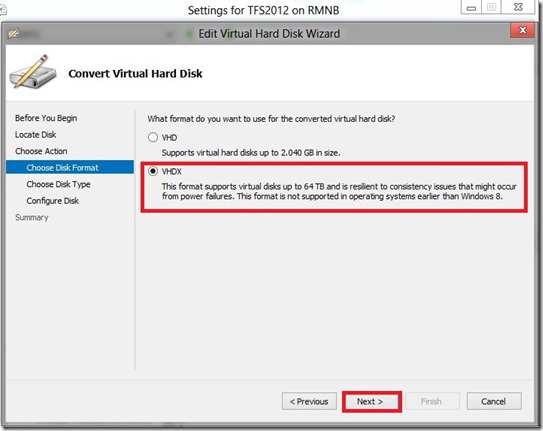
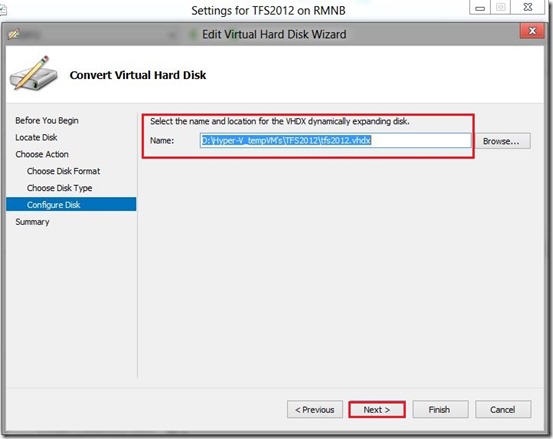
If you don’t like command line you can use Hyper-V management console or even better Virtual Machine Manager console to connect to your Hyper-V Server 2012.
Of course, there are third-party tools, like 5nine, vtUtilities… that can maintain Hyper-V Server remotely.
Few words about Hyper-V Server 2012.
Hyper-V Server is a dedicated stand-alone product that contains the hypervisor, Windows Server driver model, virtualization capabilities, and supporting components such as failover clustering, bud doesn’t contain the robust set of features and roles as the Windows Server operating system.
Differences between Microsoft Windows Server 2012 with Hyper-V role installed and Hyper-V Server 2012:
– There is no GUI. You use PowerShell, SConfig, or remote administration to manage the machine.
– There are no free virtualization rights to install Windows Server in guest OS’s on this machine. This means it is good for labs, VDI, Linux hosting and upgrading older hosts without SA.
– It is stripped down so it is just a Hyper-V host and nothing else.
I hope that you will enjoy in Windows Hyper-V Server 2012 ![]()